Monkeypox 2022 global epidemiology; Report 2022-06-24
From the Global.health team (info@global.health) • Permalink
Summary
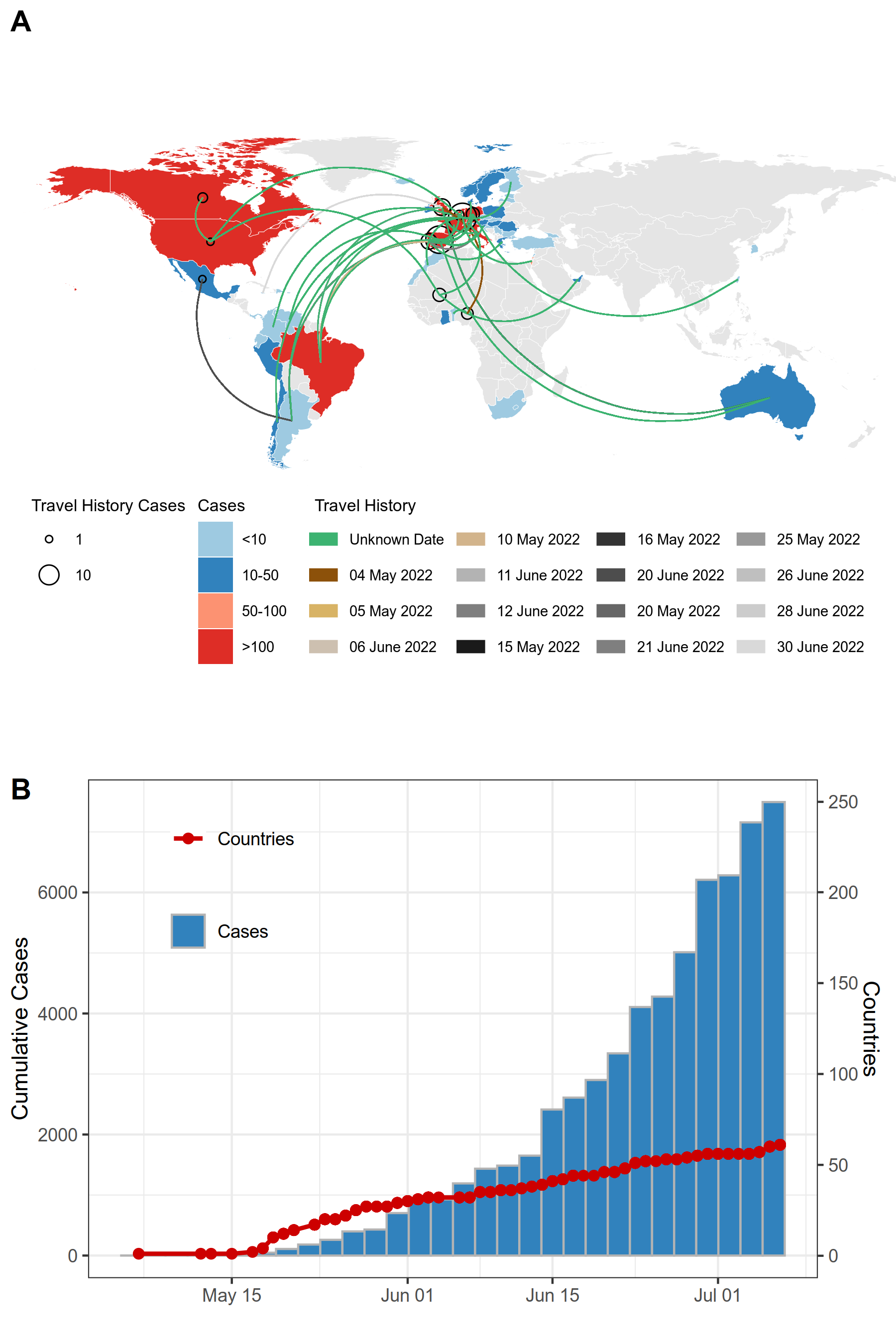
The Monkeypox 2022 outbreak has to date been detected in 59 countries (either confirmed or suspected cases), with 47 confirming transmission, 9 countries continuing to have suspected cases only, and 25 countries having discarded cases that were suspected. Overall there are 3503 confirmed and 115 suspected cases (as of 2022-06-24; Figure 1A). Since 2022-06-22, 188 new confirmed cases have been reported, and 1 new country has been added to the list (South Africa) (Figure 1B).
Turn over for figure →
| Country | Confirmed | % difference in cases compared to last week |
|---|---|---|
| England | 766 | 39 |
| Germany | 592 | 75 |
| Spain | 520 | 4 |
| France | 330 | 80 |
| Portugal | 317 | 14 |
| Canada | 223 | 33 |
| Netherlands | 167 | 75 |
| United States | 156 | 56 |
| Italy | 85 | 77 |
| Belgium | 77 | 48 |
| Switzerland | 46 | 64 |
| Ireland | 28 | 180 |
| Scotland | 18 | 12 |
| United Arab Emirates | 13 | 0 |
| Denmark | 13 | 62 |
| Israel | 13 | 160 |
| Australia | 13 | 0 |
| Austria | 12 | 200 |
| Poland | 12 | 0 |
| Brazil | 11 | 266 |
| Sweden | 10 | 0 |
| Mexico | 9 | 200 |
| Slovenia | 8 | 14 |
| Wales | 6 | 0 |
| Hungary | 6 | 100 |
| Czech Republic | 6 | 0 |
| Romania | 5 | 66 |
| Ghana | 5 | 0 |
| Argentina | 5 | 0 |
| Finland | 4 | 33 |
| Iceland | 3 | 0 |
| Northern Ireland | 3 | 50 |
| Latvia | 2 | 0 |
| Norway | 2 | 0 |
| Greece | 2 | 0 |
| Malta | 2 | 100 |
| Morocco | 1 | 0 |
| Gibraltar | 1 | 0 |
| Georgia | 1 | 0 |
| Luxembourg | 1 | 0 |
| Venezuela | 1 | 0 |
Table 1: Number of confirmed cases by country (highest to lowest) and percentage change since last week.
Of the 3503 number of confirmed cases, 127 reported travel history. For 83 cases, travel history location was unknown.
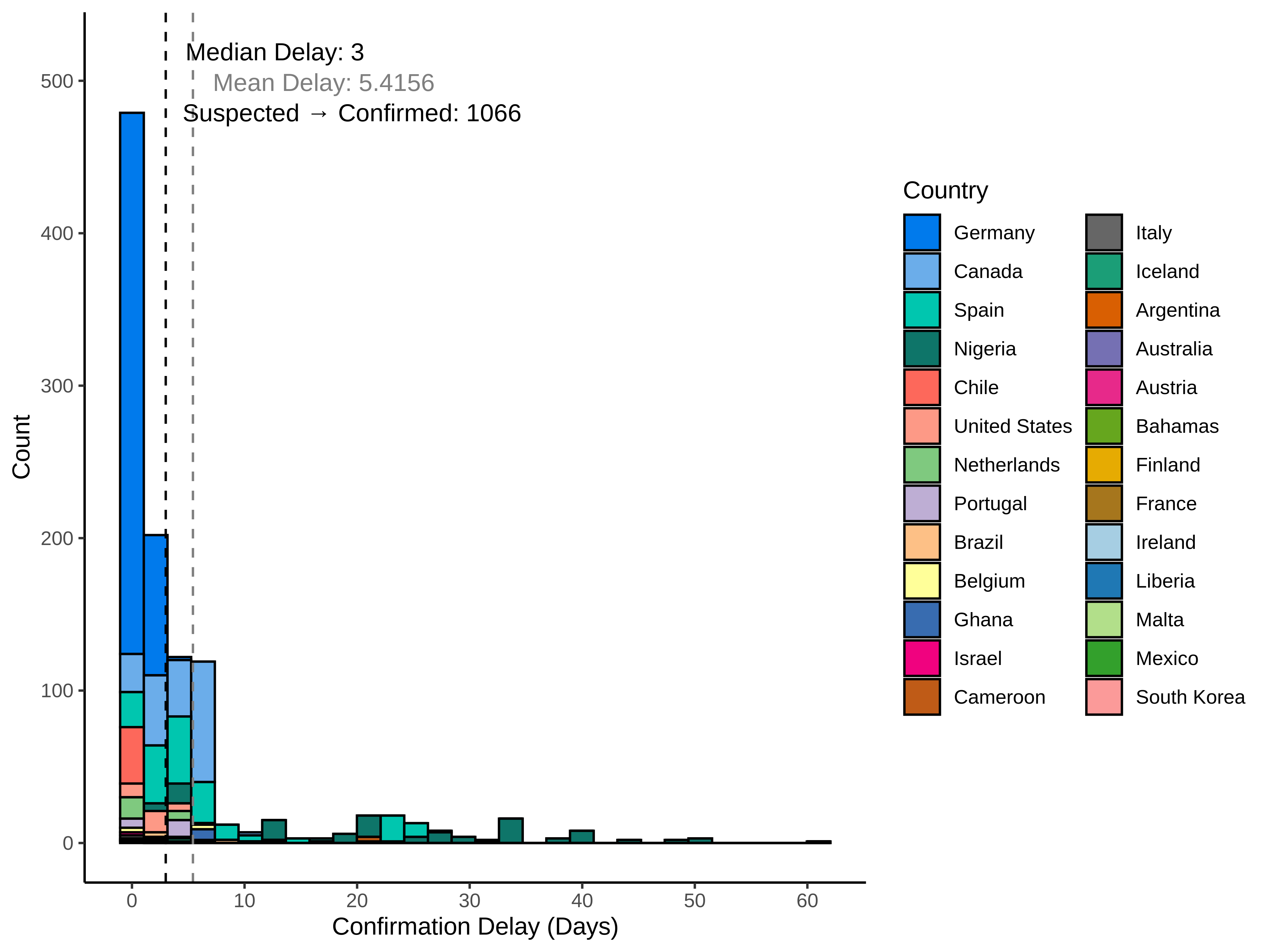
The mean delay between confirmation and entry of suspected case was 3.39 days (median 3 days) and varied by country (n = 390 total number of cases where the dates of suspected and confirmed was known; Figure 2). Most countries do not report suspected cases.
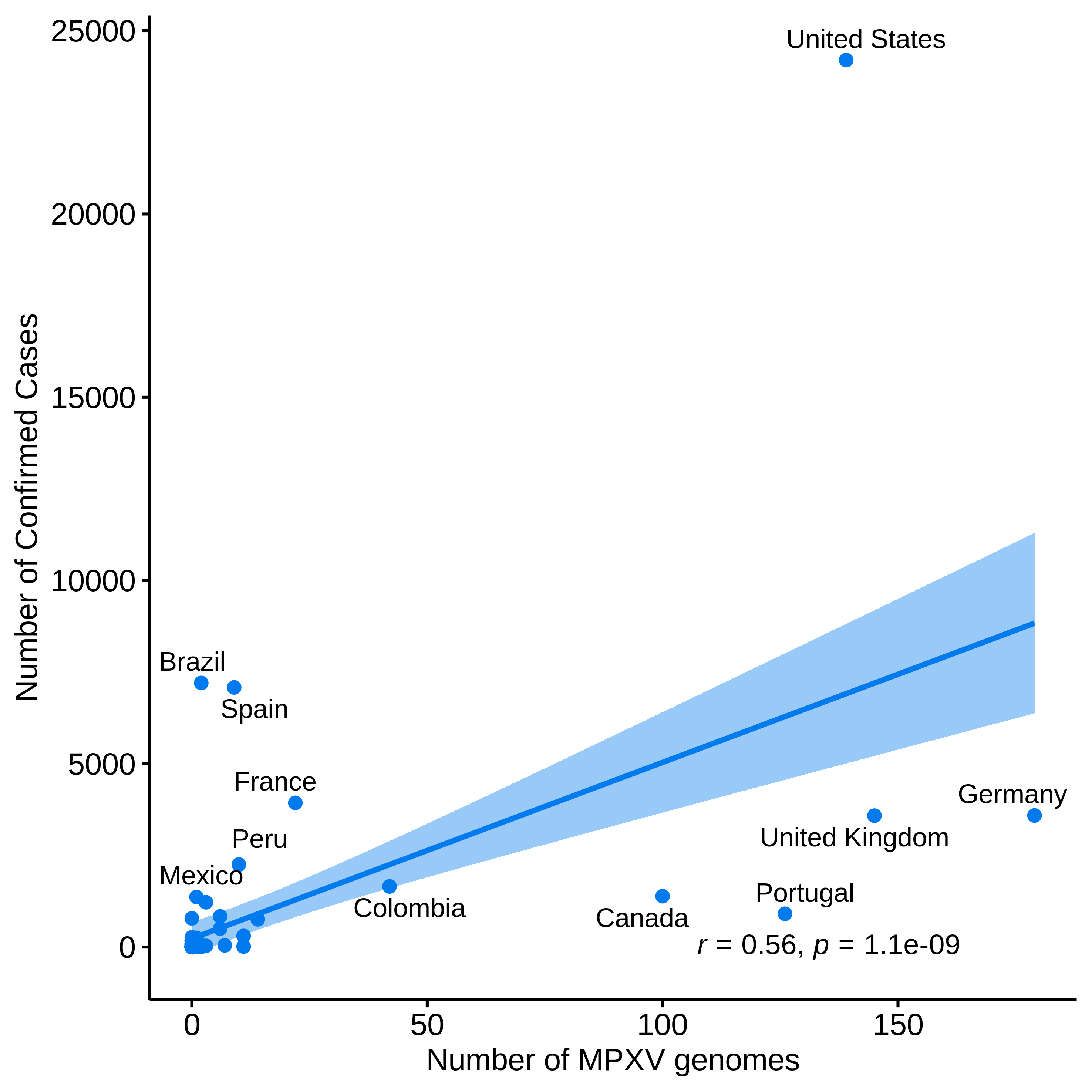
Genomic data is being reported via multiple open source repositories. In order to support ongoing genomic surveillance and improve representativeness of genomic sequences we here plot the relationship between number of genomic sequences vs. number of confirmed cases (Figure 3). The (combined) number of genomic sequences of the current outbreak is 180. The country with the highest number of genomic sequences reported is Germany. A comparison between the number of genomes and number of confirmed cases is below (Figure 3).
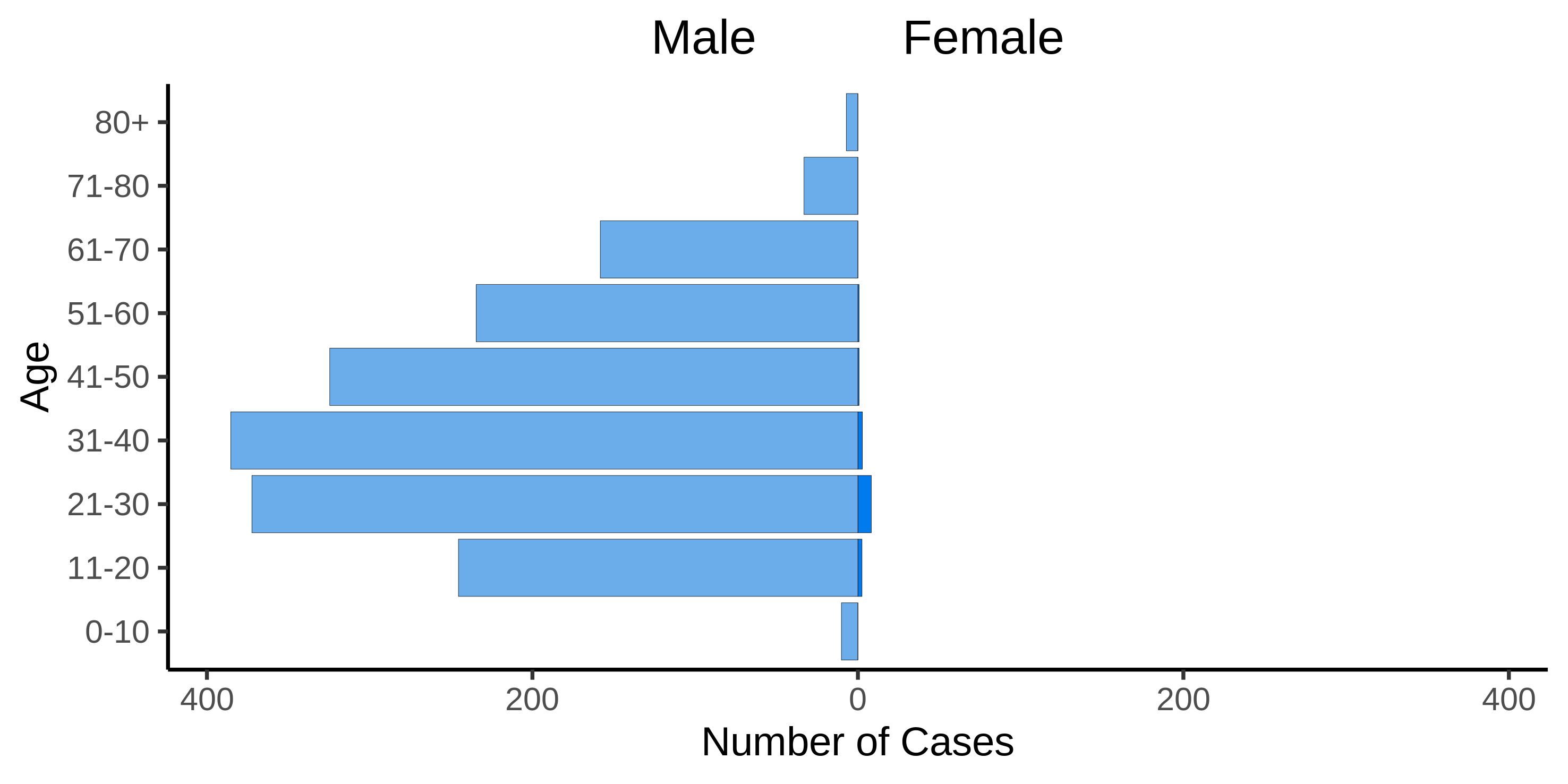
The age and gender ratio is shown in Figure 4. 98 percent of cases (for which there was an entry for
gender) are described as male. The mean age of confirmed cases is 40.
Data accessibility and reproducibility: All data used in this report are available from: https://github.com/globaldothealth/monkeypox. Should you identify any issues or have questions please raise an issue on GitHub or write to us: info@global.health. Latest data can be downloaded from here: https://github.com/globaldothealth/monkeypox/blob/main/latest.csv
Please see a description of the data curation process here: https://www.thelancet.com/journals/laninf/article/PIIS1473-3099(22)00359-0/fulltext